This article will tell you everything you need to know about low blood sugar, including what causes it, how to spot it, how to diagnose it, and how to treat it.
What Is Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)?
Hypoglycemia, which is another name for low blood sugar, is a condition that happens when there isn’t enough glucose in the blood. It is a common problem among people with diabetes, especially if taking insulin. A blood sugar reading below 4 mmol/L or 70 mg/dl is considered low. [1]
Causes of Low Blood Sugar
There are a few different causes of low blood sugar or hypoglycemia: [2]
- Eating too little food,
- Missing meals
- Delaying meals
- Taking certain medications, or
- Exercising either unplanned or too much.
- Taking too much insulin or other diabetes medications
- Drinking alcohol
Sometimes there can be no cause identified.
In some cases, hypoglycemia can be caused in patients without diabetes. If hypoglycemia is caused by an underlying medical condition, then it is important to identify and treat the underlying condition to prevent further episodes of hypoglycemia. [2]
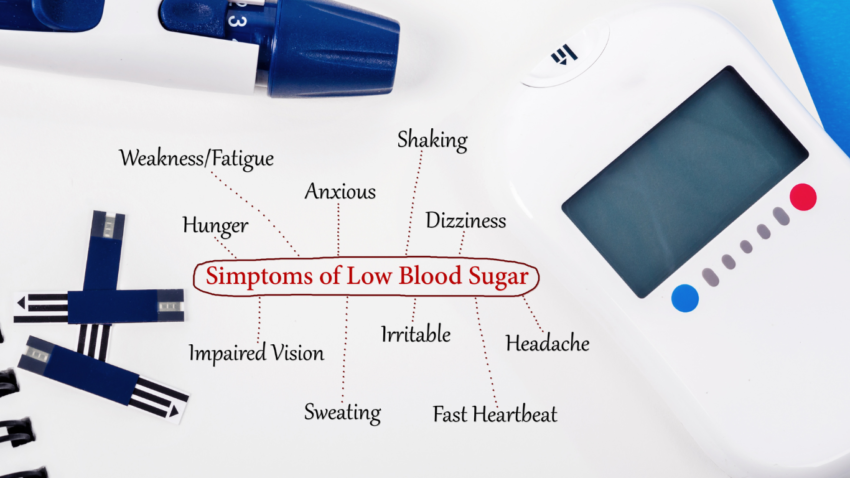
Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar
The symptoms of low blood sugar can vary depending on the person and the severity of the hypoglycemia. Signs and symptoms can be divided into early and late. [3]
Early signs and symptoms:
- lightheadedness,
- dizziness,
- turning pale
- heart beating fast or strongly (palpitation)
- sweating,
- hunger,
- shakiness,
- feelings of panic
- difficulty concentrating
- headache, and
- irritability
Late signs and symptoms
Late signs and symptoms occur if low blood sugar is not treated. People may experience:
- confusion,
- blurred vision,
- slurred speech,
- weakness
- Fits or seizure, and
- losing consciousness
It is important to know that low blood glucose can occur during sleep as well. A person can experience:
- sweating causing damp sheet,
- broken sleep,
- headache, and
- tiredness in the morning
If low blood sugar is not treated quickly, it can lead to more severe symptoms, such as seizures or loss of consciousness. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and take steps to treat it quickly. [3]
What to do when having hypoglycemia
If you are experiencing low blood sugar, the most important thing to do is to:
- test your blood sugar, and
- treat it quickly
A blood glucose meter should always be carried with you.
How to treat low blood sugar
After checking blood sugar, the following steps should be taken: [4]
- Eat or drink 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates. These include 1/2-1 glass of fruit juice or fizzy non-diet drinks, 4 to 5 jelly babies, 3 to 4 glucose tablets, and 1 tablespoon of sugar.
- Check your blood sugar after 15 minutes
If blood glucose is above 4 mmol/L or 70mg/dl then
- Eat a small snack containing slow-releasing carbohydrates. This includes a slice of bread, a couple of biscuits or half a sandwich.
If blood glucose is still below 4 mmol/L or 70mg/dl
- Again eat or drink 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrate
- Recheck your blood glucose after 15 minutes
It is important to document episodes of low blood sugar to understand patterns. This will help in taking steps to prevent future episodes of low blood sugar.
If your hypoglycemia is caused by a medication, then your doctor may recommend changing the dose or switching to a different medication. If your hypoglycemia is caused by an underlying medical condition, then your doctor may recommend treatment for the condition.
What to do in case you are treating someone unconscious or very drowsy with very low blood glucose
This can be a very stressful situation. It is important to remain calm and take the following steps: [5]
- Put the person who is unconscious in a recovery position
- If glucagon injection is available then use it if you know how to use it
- If glucagon injection is not available or you do not know how to use it then call emergency services or call for help
- If a glucagon injection is given then wait for 10 minutes. if a person does not wake for 10 minutes then call emergency services. If the person wakes up and can eat and drink safely then give them snacks containing carbohydrates.
if you are not sure then it is important to seek medical attention immediately either by calling medical emergency services or going to the nearest emergency room.
How to prevent low blood glucose
The following steps can help in preventing low blood sugar: [2]
- Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly.
- Do not miss meals. eat meals at consistent times.
- Check blood sugar before and after physical activity
- Eat a small carbohydrate snack before exercising
- Always carry fast-acting carbohydrates
- Understand the effect of alcohol on your blood sugars. Check blood sugars regularly after drinking alcohol and each carbohydrate snack after drinking alcohol.
It is important to speak to your healthcare provider to discuss ways to prevent low blood sugar. This may include adjusting your medications. If you have diabetes, then you should check your blood glucose levels before and after meals, and before and after physical activity.
Complications of untreated low blood sugar
If low blood glucose is not treated then it can result in: [1]
- Coma – losing consciousness
- Fits or seizures
- Death
Complications of repeated low blood sugar
If a person is suffering from repeated low blood glucose then it can lead to a condition called hypoglycemic unawareness. It is a condition where the body and brain’s ability to recognize the signs and symptoms of low blood glucose decreases. In severe cases, the person is unable to get any warning signs or symptoms of low blood sugar. [1]
If you experience repeated episodes of low blood sugar, then it is important to talk to your doctor about ways to prevent future episodes. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle modifications or changes to your medications to help prevent future episodes of hypoglycemia.
Low blood sugar and driving
Driving when your blood sugar is low can increase your risk of having a car accident. Therefore, it is important to: [6]
- Always check your blood sugar before driving.
- If your blood sugar is above 5 mmol/L or above (>90 mg/dl) then it is safe to drive.
- If blood sugar levels are between 4mmol/L to 5 mmol/L (72-90 mg/dl) then eat a snack before driving.
- Always keep your glucose meter or test strip with you in the car.
- Always keep fast-acting carbohydrates in the car.
- Take regular breaks during the long journey.
If your blood sugar is low, then it is important to make sure that you stop at a safe place. Remove the key from the ignition or turn the car off. Move to the passenger side. Treat your low blood glucose as usual. Do not drive for 45 minutes after the blood glucose is above 5 mmol/L or 90 mg/dl.
References and Further Reading
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.). Low Blood Glucose (Hypoglycemia).
- Mayo Clinic. (2023, November 18). Hypoglycemia.
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar).
- American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Low Blood Glucose (Hypoglycemia).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024, May 16). Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia).
- Diabetes UK. (n.d.). Hypoglycaemia (hypos) and driving.