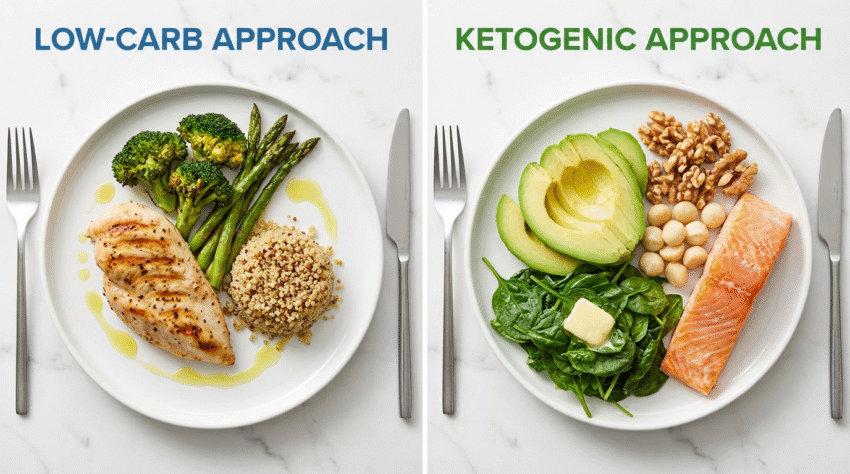
The management of insulin resistance serves as an essential requirement to stop type 2 diabetes development while it supports better metabolic wellness. The low-carbohydrate diet together with the ketogenic (keto) diet function as two widely recognized dietary methods which people use for health advantages. The two methods require carbohydrate restrictions but they produce different nutritional profiles which produce distinct effects on body functions. Your selection of an appropriate health plan depends on your understanding of these differences. ## Understanding Insulin Resistance The hormone insulin functions to transfer glucose from blood circulation into cells so they can produce energy. Your cells fail to respond properly to insulin when you develop insulin resistance which results in elevated blood sugar levels. The body produces insulin resistance because of this condition which leads to prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. The body develops insulin resistance because of high consumption of processed carbohydrates and sugary foods which triggers continuous high insulin production [1].## The Low-Carbohydrate Approach A low-carbohydrate diet restricts the consumption of sugary foods and pasta and bread but allows more flexibility than a ketogenic diet. There is no exact definition for low-carb diets because they usually limit daily carbohydrate consumption to between 50 and 150 grams. The diet needs to focus on eating whole natural foods which consist of non-starchy vegetables and lean proteins and healthy fats. The low-carb diet functions to decrease blood sugar and insulin levels through its method of carbohydrate restriction. The body can show better insulin sensitivity because it avoids the need to constantly handle elevated glucose levels. Research indicates that low-carb diets help people with insulin resistance lose weight while improving their blood sugar control [2]. | Feature | Low-Carbohydrate Diet | Ketogenic Diet || :— | :— | :— | | **Daily Carbs** | 50-150 grams |
Low-Carb vs. Keto: Which Diet Is Better for Managing Insulin Resistance?
Tags: